Optimisation of a trading strategy is the process of adjusting the parameters of a strategy to achieve the best performance.
Why should you optimise a strategy?
There are several reasons for running an optimisation of a trading strategy.
- Identify the best set of parameters for a strategy, which can lead to improved performance.
- Help identify any potential issues with a strategy, such as overfitting or poor risk management.
- Identify the best trade entry and exit points, which can improve the accuracy and distribution of the strategy.
Optimisation example
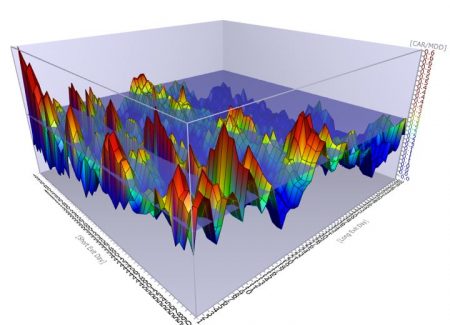
Source: Frame Funds Management Research
Why shouldn’t you optimise a trading strategy?
There are some reasons against running an optimisation of a trading strategy.
- Computationally expensive, especially for complex strategies.
- Optimization can lead to overfitting, which can result in poor performance on new, unseen data. This is because the optimizer may find a set of parameters that fit the historical data well but not the future data.
- Over-parametrised. When you run an optimisation, generally strategy complexity increases, which reduces sample size, increasing in-sample returns and performance statistics. This may not reflect well during out of sample testing.
In summary, Optimisation of a trading strategy can lead to improved performance and risk management. However, it also has its drawbacks, such as the potential for overfitting and computational expense. It’s crucial to use techniques like in-sample, out-of-sample, and walk-forward testing to ensure that the strategy is robust enough to changing market conditions.